|
|
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|||
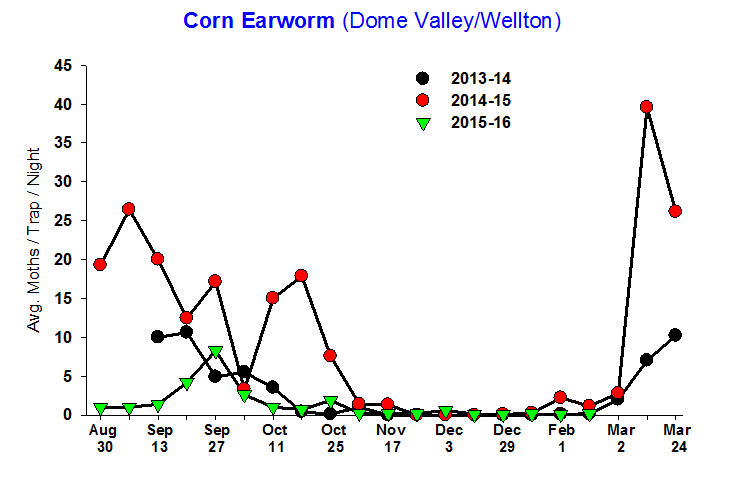
With local temperatures beginning to increase, insect activity should also start to pick up. Even though worm pressure has been light in the field for the past month or so, it would be wise to keep a look out for corn earworm (CEW). In the past few years, unusually high CEW abundance has been reported by PCAs on late head lettuce, particularly in the Dome/Wellton areas. Our latest trap catches from the Areawide Trap Network indicate that moth counts have been nearly bottomed out for some time. However, this is typical for February (see graph below), and could be the calm before the storm. In the previous two spring seasons, trap catches started to increase in late February-early March, and peaked by mid-to-late March. These increased trap numbers should be used as an early indicator that moths are actively flying at night at higher abundance and PCAs should start to scout more aggressively for eggs and larvae. CEW can be very damaging in spring crops once head formation begins; larvae will usually bore into the head 1-2 days upon hatching. Corn earworm is much more likely to bore into lettuce heads than other Lepidoptera larvae, rendering the heads unmarketable. If fields are not watched closely, infestations may not be noticed until the head is harvested. Once inside the head, control of larvae with currently available insecticides is not possible. Thus, pay careful attention for newly oviposited eggs (laid singly) on lettuce plants. If you are beginning to find eggs and suspect that CEW are active in the field when plants are beginning to head, it would be a good idea to treat at regular spray intervals (~ 7days). The UA nominal threshold for CEW in head lettuce from early heading to harvest is 1-2 larvae / 100 plants. Essentially, you see one, you spray. Repeated insecticide treatments may be required to maintain low population levels near harvest. Most contact insecticides recommended for Lep larvae are active against CEW. Furthermore, the addition of a pyrethroid with thrips, aphid and/or fungicide sprays may be cheap insurance against larvae infesting heads as you approach harvest. For more information on CEW management and control recommendations see Corn Earworm Management on Desert Production and the 2016 Lep Control Chart. |
|||
| Back | |||
|
For questions or comments on any of the topics please contact Marco Pena at the Yuma Agricultural Center.
|
|||
|
Home |
Cotton | Veggies |
Forages | Grains
| Citrus |
Crop x Crop Insects | Diseases| Weeds | Pesticides | Economics | News | Weather | Research | Photos | Contacts | General Info. Copyright © 2001 University of Arizona, College of Agriculture and Life Sciences Webmaster: Al Fournier (acis@ag.arizona.edu) |
|||